Which Best Describes Lateral Inhibition in Sensory Processing
Which best describes lateral inhibition in the somatic sensory system. Inhibitory interneurons decrease action potentials from receptors at the periphery of a stimulated region.
The precision of locating a stimulus is increased by inhibiting.

. Lateral inhibition is the inhibition of a certain developmental process in one cell induced by signals from an adjacent cell. Lateral inhibition is the process by which stimulated neurons inhibit the activity of nearby neurons. Lateral inhibition is the ability of excited neurones to inhibit the activity of neighbouring neurones.
Which best describes lateral inhibition in the somatic sensory system. This occurs at various levels of the visual system. Lateral inhibition enables the brain to manage environmental input and avoid information overload.
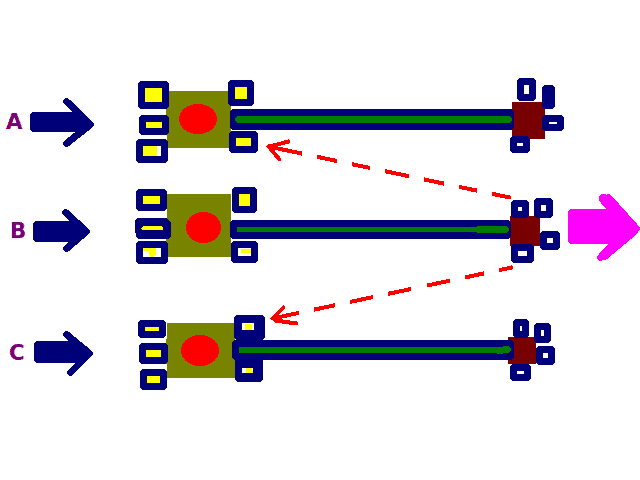
When a stimulus is maintained for a long time action potentials from sensory receptors decrease in. Those sensory neurons whose receptive fields are stimulated most strongly inhibitvia interneurons that pass laterally within the CNSsensory neurons that serve neighboring receptive fields. Consequently there exists an increased contrast in excitation between neighbouring neurones allowing better sensory acuity.
Cortical layer 1 L1 interneurons have been proposed as a hub for attentional modulation of underlying cortex but the transformations that this. Which best describes lateral inhibition in sensory processing. All-Optical Electrophysiology Reveals the Role of Lateral Inhibition in Sensory Processing in Cortical Layer 1.
In neurobiology lateral inhibition is the capacity of an excited neuron to reduce the activity of its neighbors. Lateral inhibition is a common theme in sensory physiology. Which best describes lateral inhibition in sensory processing.
Asked Sep 4 2019 in. To understand the lateral inhibition process start with intensity coding. In lateral inhibition nerve signals to neighboring neurons positioned laterally to the excited neurons are diminished.
Lateral inhibition reduces the contrast between the frequency of action potentials generated at the center of a stimulus and the frequency of action potentials in surrounding pathways. This prevents the spread of neuronal activity laterally. A process in which lateral connections allow one photoreceptor to inhibit the responsiveness of its neighbor thus enhancing the sensation of visual contrast.
This creates a contrast in stimulation that allows increased sensory perception. When a stimulus is maintained for a long time action potentials from sensory receptors decrease in. Asked Sep 25 2016 in Anatomy Physiology by RenegadeMaster.
The frequency of action potentials along pathways from the site of a stimulus is increased by lateral inhibition. It is also referred to as lateral antagonism and occurs primarily. What is lateral inhibition and why is it important in perception.
Lateral inhibition refers to the capacity of excited neurons to reduce the activity of their neighbors. Presynaptic axoaxonal synapses reduce neurotransmitter release at excitatory synapses. Lateral inhibition disables the spreading of action potentials from excited neurons to neighboring neurons in the lateral direction.
Lateral inhibition is a CNS process whereby application of a stimulus to the center of the receptive field excites a neuron but a stimulus applied near the edge inhibits it. What is a potential function of lateral inhibition quizlet. Lateral inhibition and the resultant sharpening of sensation occur within the central nervous system.
Lateral inhibition plays an important role in visual perception by increasing the contrast and resolution of visual stimuli.

Lateral Inhibition Sharpening Of Signal Human Anatomy And Physiology Medical Studies Physiology
Sensory Acuity Lateral Inhibition Two Point Discrimination Teachmephysiology

No comments for "Which Best Describes Lateral Inhibition in Sensory Processing"
Post a Comment